ISO 26262
Safety is one of the key issues for the future development of automobiles, not only in the fields of driving assistance and power drive, but also in the fields of vehicle dynamic control and active& passive safety systems. New features are increasingly touching on the field of system safety engineering. The development and integration of these features will strengthen the need for security related system development processes and the need for to provide evidence that functional safety objectives are satisfied. ISO 26262 can help avoids risks by providing appropriate requirements and processes.
ISO26262 is a functional safety standard specifically designed for automotive EE and software components, developed based on the ISO/IEC61508 standard by numerous international vehicle manufacturers (Volkswagen, BMW, Volvo, General Motors, Ford, Toyota, Honda, etc.) and automotive suppliers (Bosch, Continental, TRW, etc.) to address increasingly complex automotive functional safety issues. The standard was first officially released in 2011 and the latest second version was released in 2018.
ISO 26262 applies to all activities during the safety lifecycle of safety-related systems comprised of electrical, electronic and software components. With regard to enterprises, ISO26262:
a) Provides a car safety lifecycle (management, development, production, operation, service, decommissioning) and supports the tailoring of necessary activities during these lifecycle phases;
b) provides an automotive-specific risk-based approach to determine integrity levels [Automotive
Safety Integrity Levels (ASILs)];
c) uses ASILs to specify which of the requirements of ISO 26262 are applicable to avoid unreasonable residual risk;
d) Provides requirements for validation and recognition measures to ensure a sufficient and acceptable level of security is achieved;
e) Provides requirements related to suppliers.
The achievement of functional safety is influenced by the development process (including such
activities as requirements specification, design, implementation, integration, verification, validation and configuration), the production and service processes and the management processes. Safety is intertwined with common function-oriented and quality-oriented activities and work products. The ISO 26262 series of standards addresses the safety-related aspects of these activities and work products.
The core values of implementing the ISO26226 standard lies in:
Through the system's functional safety R&D management process, as well as systematic verification and validation methods for the hardware and software of the automotive electronic control system, failures of the safety functions of the electronic system are ensured to be avoided under various harsh conditions, thereby ensuring the safety of drivers, passengers, and other related personnel.
By implementing the ISO26262 standard, car manufacturers and suppliers can not only improve the safety performance of their products, but also minimize the recall risk caused by electronic component quality issues and avoid significant economic losses.
In some countries, if the latest technical requirements have been achieved through the implementation of ISO26262, relevant legal liabilities can be exempted.
Before importing ISO26262 certification, enterprises should fully consider the following aspects:
1) The object of certification belongs to products related to functional safety of electronic control units composed of electronic electrical and software components on road vehicles.
2) Before importing ISO26262 certification, the enterprise has already imported and implemented ISO9000 or IATF 16949 quality management system certification.
3) The enterprise has established a functional safety function and management system that complies with ISO26262 and relevant laws and regulations, and has been in operation for no less than 3 months.
The certification of ISO26262 is divided into functional safety management system certification and product certification.
1. Functional safety management system certification
Functional safety management system certification falls into four stages: certification application, stage 1 audit, stage 2 audit and issuance of certification certificate.
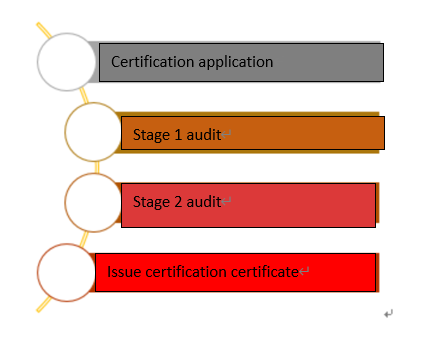
ISO 26262 Functional safety management system certification flowchart
1) Application for certification. The applicant submits the certification application and related attachments to CEPREI Certification Body, and signs the certification contract after the application is accepted.
2) Stage 1 Audit. At this phase, the auditee’s documents, grading criteria, selection criteria, etc., are reviewed. If the conclusion of stage 1 audit is that the preparation is insufficient, cannot enter into stage 2 of the on-site audit.
3) Stage 2 Audit. At this stage, the compliance and effectiveness of the auditee's management system are evaluated, and the rectification of non-conformities is ensured.
4) Issuance of certification certificates. The evaluation results will be submitted to the Technical Committee of CEPREI Certification Body for review. After being determined by the technical committee that the review has passed, the certification certificate will be issued.
2. Functional safety product certification
Functional safety product certification is divided into four steps, namely enterprise certification application, certification implementation, certification result evaluation and issuance of certification certificate.
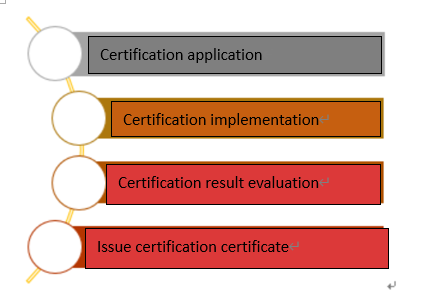
ISO 26262 product certification flowchart
1)Enterprises apply for certification. The certification client submits the certification application, and the certification contract is signed after the application is accepted by the certification body.
2) Certification implementation. CEPREI Certification Body sets up an audit team to conduct a functional safety audit on the products provided by the certification client, provides audit results, ensures the correction of non-conformities.
3) Evaluation of certification results. CEPREI Certification Body evaluates the audit results to determine whether relevant certification can be granted.
4) Evaluation of certification results. After passing the certification, CEPREI Certification Body will issue a certification certificate to the certification client.
CEPREI Certification Body (hereinafter referred to as "CEPREI") is a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Fifth Electronics Research Institute of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, specializing in training, certification and technical services. Since CEPREI introduced the concept of "certification" into China in 1979, hundreds of thousands of certificates of various types have been issued to tens of thousands of enterprises at home and abroad.
There are more than 500 full-time and part-time auditors and technical service personnel, 27 CMMI/Automotive SPICE assessors and more than ten ISO26262 functional safety specialists in CEPREI. It has provided R&D capability assessment and functional safety-related technical services for more than 1,700 enterprises. CPEREI has offices in more than 30 cities across the country, and its business covers all provinces and cities in the country.
In 1998, CEPREI Certification Body was authorized by the three major automobile manufacturers to carry out QS9000 certification, which opened the business of CEPREI in the automotive field. Up to now, CEPREI has more than 20 years of experience in this field. At present, the main business of CPEREI in the automotive field includes:
Management systems certification: IATF16949 automotive quality management system, ISO26262 management system;
Software R&D process assessment : Automotive SPICE, CMMI, TMMi (Testing Capability Maturity);
Product certification: ISO26262 product certification, AEC-Q200 automotive electronic components certification;
Information security: code security audit, information security risk assessment, information security penetration test, ISO/IEC 27001 certification;
Training business: Automotive SPICE training, ISO26262 training, CMMI training, Certified Software Quality Engineer (CSQE) training, Certified Professional for Requirements Engineering (CPRE) training, international software testing engineer (ISTQB) training, Certified Software Cost Estimate Professional (CCEP) training, agile software development (SCRUM Master) training.